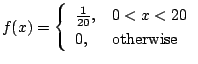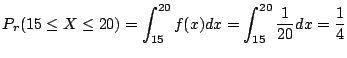Next: 正規分布の応用(Application of normal distribution) Up: 理論分布 Previous: ポワソン分布(Poison distribution) 目次
確率変数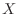 の確率密度関数が
の確率密度関数が
![$\displaystyle g(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi} \sigma} EXP\left[-\frac{(x-\mu)^2}{2 \sigma^2}\right], -\infty < x < \infty $](img139.png)
で与えられるとき,確率変数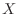 は正規分布(Normal distribution)に従うといい,
は正規分布(Normal distribution)に従うといい,
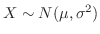 と表わします.
と表わします.
また,
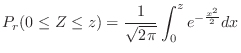
標準化
確率変数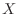 の平均
の平均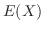 を0に,分散
を0に,分散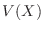 を1に直すことを標準化といいます.
を1に直すことを標準化といいます.
標準化の方法(method of normalization)
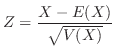
とおくと
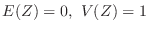
一様分布
確率変数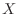 の確率密度関数が
の確率密度関数が
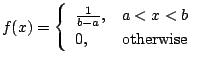
で与えられるとき,確率変数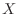 は一様分布(uniform distribution)に従うといい,
は一様分布(uniform distribution)に従うといい,
![]() と表わします.
と表わします.
解 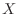 を電車の待ち時間とすると,
を電車の待ち時間とすると,
![]() である.このとき,
である.このとき,