Next: Trigonometric Function Up: Functions Previous: Functions Contents Index
| Functions |
|---|
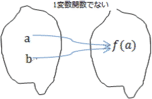
For each variable 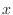 in in
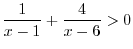 , there is exactly one , there is exactly one 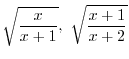 so that the ordered pair so that the ordered pair 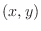 is contained in the subset defining rule is contained in the subset defining rule 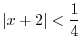 . This rule is called function and denoted by . This rule is called function and denoted by 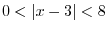 . .
|
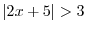 is called an independent variable, The value
is called an independent variable, The value 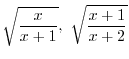 determined by
determined by 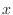 is called the dependent variable. If
is called the dependent variable. If 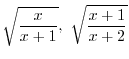 is a function of
is a function of 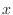 ,
,
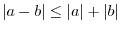
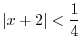 and
and
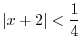 .
.
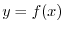
SOLUTION To find the domain of 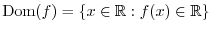 , it is enough to find the set of variables
, it is enough to find the set of variables 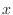 so that
so that
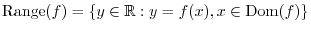 is also real. Note that for
is also real. Note that for
 ,
, 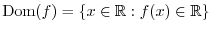 is real.
is real.
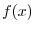 imples that
imples that
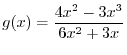 . Thus,
. Thus,
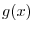
Using the intervals' notation, we have
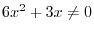
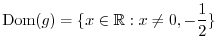
SOLUTION 1.
Note that
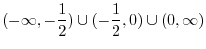 is real whenever the denominator is not 0 and
is real whenever the denominator is not 0 and
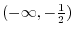 .
With these conditions, we have
.
With these conditions, we have 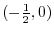 . Rewriting to get
. Rewriting to get 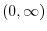 . Using the interval,
. Using the interval,
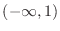

2.
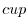 is real whenver the denominator is not 0 and the inside the radical has to be non-negative. With these conditions,
is real whenver the denominator is not 0 and the inside the radical has to be non-negative. With these conditions,
 and
and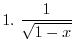
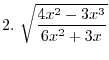
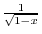
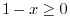
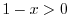 and
and
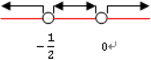
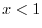 , we have the denominators 0. Thus these values do not satisfy the inequality. We put circle on the number line. On the other hand,
, we have the denominators 0. Thus these values do not satisfy the inequality. We put circle on the number line. On the other hand,
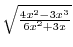 satisfies the inequality, we put dot on the number line to indicate this number is included. Now we check the sign
satisfies the inequality, we put dot on the number line to indicate this number is included. Now we check the sign
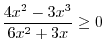 .
.
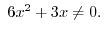
Using the interval, we have
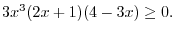
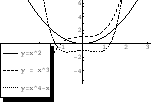
NOTE The graph of the function Graph
For a function 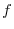 , the set of points
, the set of points 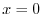 on the
on the 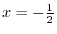 -plane is called the graph. of a function
-plane is called the graph. of a function 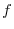 .
.
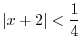 is one way to express the rule between two sets. To draw a nice graph, one must know about the critical points, concave up, concave down.
is one way to express the rule between two sets. To draw a nice graph, one must know about the critical points, concave up, concave down.
NOTE The range of Composite Function
For the range of 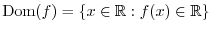 is in the domain of
is in the domain of 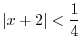 , the correspondense between
, the correspondense between  and
and 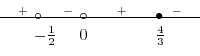 is called the composite function and denoted by
is called the composite function and denoted by 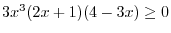 .
.
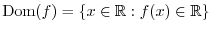 has to be in the domain of
has to be in the domain of 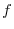 . Otherwise,
. Otherwise,  can not be defined.
can not be defined.
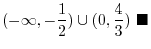 ,
,
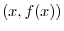 . Find
. Find
 and
and
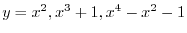 .
.
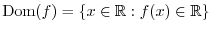 is
is
 and these are in the domain of
and these are in the domain of 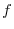 . Thus,
. Thus,
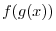
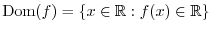 is
is
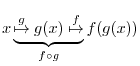 , the range of
, the range of 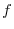 given by
given by
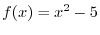 is not in the domain of
is not in the domain of 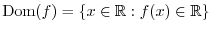 . Then, exclude the value of
. Then, exclude the value of 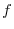 which becomes 0, the range of
which becomes 0, the range of 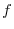 is in the domain of
is in the domain of 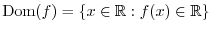 . So, for
. So, for
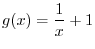 , we have
, we have
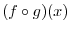 |
 |
 |
|
 |
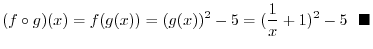 |
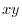 .
.
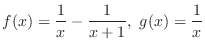
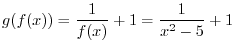
SOLUTION 1.
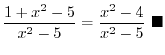
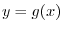
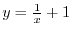
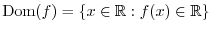 , for
, for
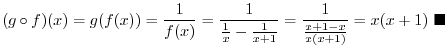 , we have
, we have
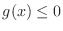 . Also, for
. Also, for 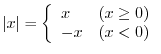 or
or 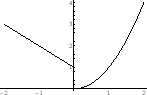 , we have
, we have 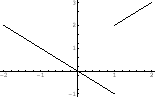 . Thus,
. Thus,
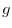
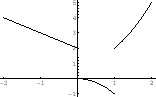 , we obtain
, we obtain
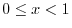
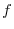 , for
, for 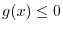 , we have
, we have
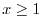 . Also, for
. Also, for 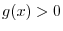 , we have
, we have
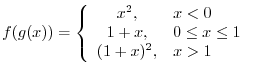 , and for
, and for  , we have
, we have
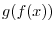 . Therefore,
. Therefore,
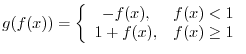
| One-to-one Function |
|---|
For any
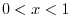 , ,
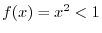
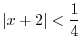 is said to be one-to-one. is said to be one-to-one.
|
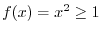 is
is
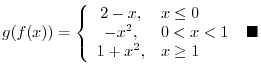 Thus, once we show that the contrapositive is true whenever the original statement is true, we can use the contrapositive.
1.1
Thus, once we show that the contrapositive is true whenever the original statement is true, we can use the contrapositive.
1.1
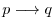
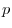
SOLUTION 1. For
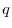 , we have
, we have
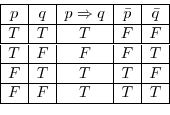 . Thus, it is not on-to-one
. Thus, it is not on-to-one

2. Suppose that
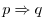 . Then
. Then
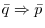 . Multiply
. Multiply
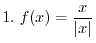 to the both sides, we have
to the both sides, we have
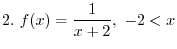 . Thus
. Thus
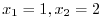

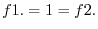
SOLUTION We show
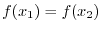 .
.
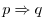 implies that
implies that
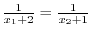 which implies that
which implies that
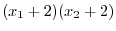 . Now we have show
. Now we have show
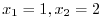 is the only solutioin. To show this, we write
is the only solutioin. To show this, we write
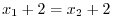 . Then we have
. Then we have
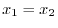 . This is sums of squres. Thus they are never 0 except
. This is sums of squres. Thus they are never 0 except
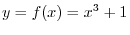 . This shows that
. This shows that
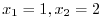 is the only solution.
is the only solution.

NOTE The inverse function of Inverse Function
For a function 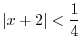 is one-to-one, the correspondence
is one-to-one, the correspondence 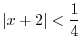 between each
between each
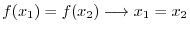 and unique
and unique  such that
such that 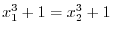 is called the inverse function of
is called the inverse function of 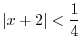 and denoted by
and denoted by 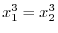 .
.
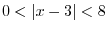 is
is 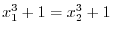 and satisfies
and satisfies
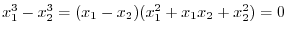 . Thus we can write
. Thus we can write
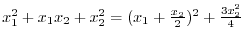
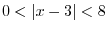 , we can simply change
, we can simply change  and
and 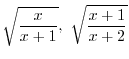 and solve for
and solve for 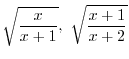 . This way we can find the inverse function of
. This way we can find the inverse function of 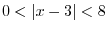 .
.
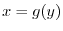
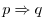 . Then
. Then
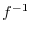 . Now multiply both sides by
. Now multiply both sides by
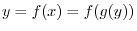 and simplify the equation to get
and simplify the equation to get
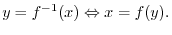
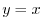
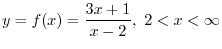 . Thus
. Thus
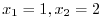 .
.
Next we find the inverse 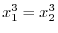 . Using
. Using
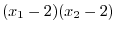 to obtain
to obtain
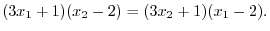
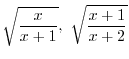 , we get
, we get
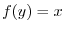 . Then
. Then
 and
and
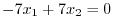
 1.2
1.2
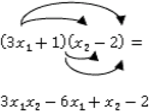
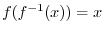
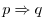 . Then
. Then
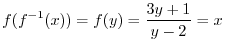 . Clearing denominators, we have
. Clearing denominators, we have
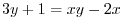 which implies that
which implies that
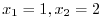 . Thus one-to-one.
We next find the inverse function. Replace
. Thus one-to-one.
We next find the inverse function. Replace 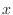 by
by 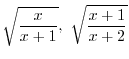 , we get
, we get
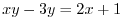 which implies that
which implies that
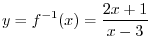 . Now take the reciprocal of both sides, we have
. Now take the reciprocal of both sides, we have
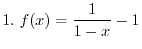 which implies that
which implies that
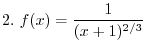
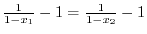 . Thus this is not one-to-one
. Thus this is not one-to-one

|
ExercisesA
|
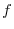 when the value of
when the value of  is 1?D
is 1?D
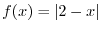 and
and
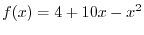 , draw the graph of the following functions?D
(a)
, draw the graph of the following functions?D
(a)
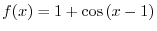 (b)
(b)
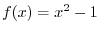
 and
and 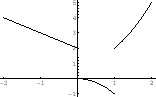 ?D
?D
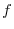 is called even function provided
is called even function provided
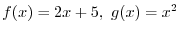 in
in
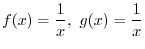 . On the other hand if
. On the other hand if
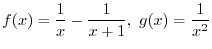 , then the function is called odd function. Determine the following functions are even or odd functions.
, then the function is called odd function. Determine the following functions are even or odd functions.
|
ExercisesB
|
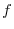 ?D
?D
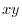 and
and 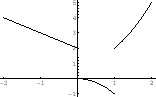 ?D
?D
(a) A product of even function and odd function?D