Next: 2.2 導関数の計算 Up: 確認問題詳解 Previous: 1.6 超越関数 索引
1.
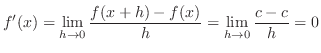
 |
 |
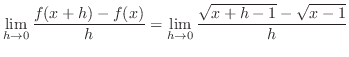 |
|
 |
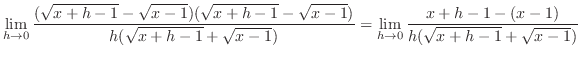 |
||
 |
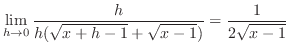 |
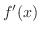 |
 |
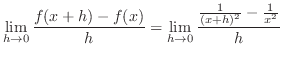 |
|
 |
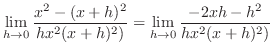 |
||
 |
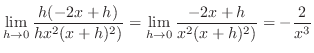 |
2.
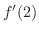 |
 |
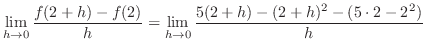 |
|
 |
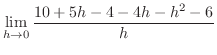 |
||
 |
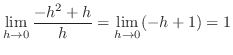 |
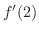 |
 |
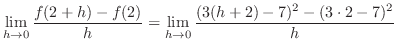 |
|
 |
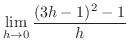 |
||
 |
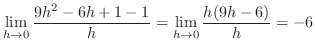 |
3.
(a) 接線の方程式は,接線が通る点
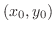 と傾き
と傾き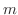 が与えられると,
が与えられると,
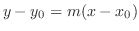 で求めることができる.
で求めることができる.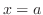 における接線の傾き
における接線の傾き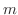 は
は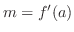 で与えられる.そこで,まず,
で与えられる.そこで,まず,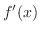 を求めると,
を求めると,
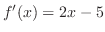 より,
より,
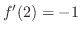 .次に,接線は点
.次に,接線は点
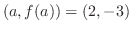 を通るので,求める接線の方程式は
を通るので,求める接線の方程式は
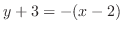 .整理すると
.整理すると
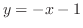 となる.
となる.
(b) 接線の方程式は,接線が通る点
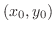 と傾き
と傾き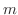 が与えられると,
が与えられると,
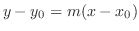 で求めることができる.
で求めることができる.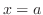 における接線の傾き
における接線の傾き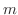 は
は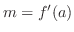 で与えられる.そこで,まず,
で与えられる.そこで,まず,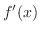 を求めると,
を求めると,
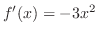 より,
より,
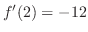 .次に,接線は点
.次に,接線は点
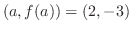 を通るので,求める接線の方程式は
を通るので,求める接線の方程式は
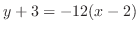 .整理すると
.整理すると
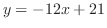 となる.
となる.
(c) 接線の方程式は,接線が通る点
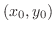 と傾き
と傾き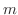 が与えられると,
が与えられると,
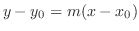 で求めることができる.
で求めることができる.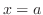 における接線の傾き
における接線の傾き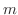 は
は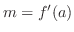 で与えられる.そこで,
で与えられる.そこで,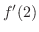 を求める.
を求める.
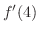 |
 |
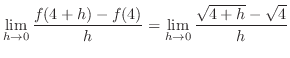 |
|
 |
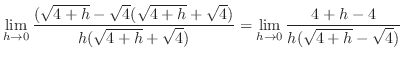 |
||
 |
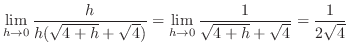 |
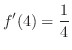 .次に,接線は点
.次に,接線は点
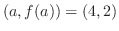 を通るので,求める接線の方程式は
を通るので,求める接線の方程式は
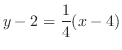 .整理すると
.整理すると
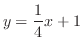 となる.
となる.
4.
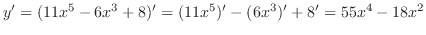
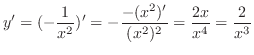
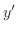 |
 |
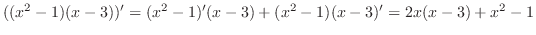 |
|
 |
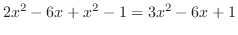 |
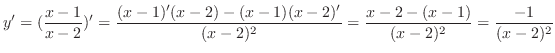
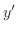 |
 |
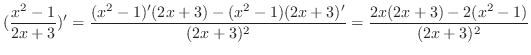 |
|
 |
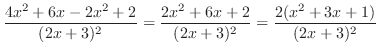 |
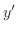 |
 |
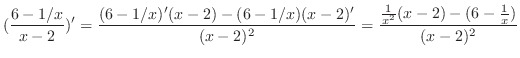 |
|
 |
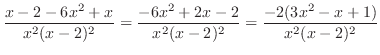 |
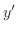 |
 |
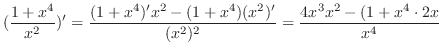 |
|
 |
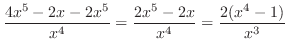 |