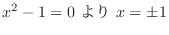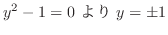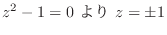6.9
1.
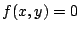 より定まる陰関数
より定まる陰関数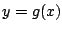 が
が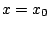 で極値
で極値
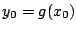 をとるならば,
をとるならば,
さらに
(a)
まず,
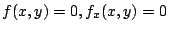 を満たす
を満たす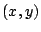 を求める.
を求める.
より
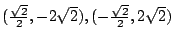 .
次に,
.
次に,
より
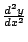 を計算すると
を計算すると
よって
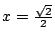 のとき
のとき
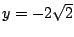 は極小値,
は極小値,
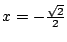 のとき
のとき
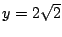 は極大値.
は極大値.
(b)
まず,
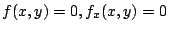 を満たす
を満たす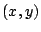 を求める.
を求める.
より
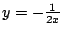 .これを
.これを
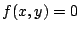 に代入すると
に代入すると
よって
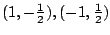 .
次に,
.
次に,
より
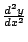 を計算すると
を計算すると
よって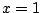 のとき
のとき
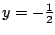 は極小値,
は極小値,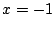 のとき
のとき
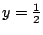 も極小値.
も極小値.
(c)
まず,
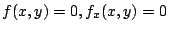 を満たす
を満たす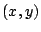 を求める.
を求める.
より
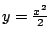 .これを
.これを
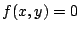 に代入すると
に代入すると
よって
![$ (0,0), (2\sqrt[3]{2}, 2\cdot2^{\frac{2}{3}})$](img2367.gif) .
次に,
.
次に,
より
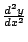 を計算すると
を計算すると
よって
![$ x = 2\sqrt[3]{2}$](img2371.gif) のとき
のとき
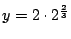 は極小値.
は極小値.
2.
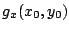 と
と
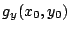 の少なくとも一方は0でないとする.
条件
の少なくとも一方は0でないとする.
条件
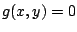 の元で,
の元で,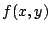 が
が
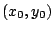 で極値をとるための必要条件は
で極値をとるための必要条件は
とおいて,
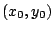 で
で
が成り立つことである.
ここで,
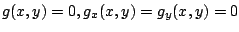 の点を特異点という.
の点を特異点という.
(a)
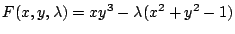 とおくと
とおくと
 のとき式(7.9)より,
のとき式(7.9)より,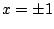 ,式(7.10)より
,式(7.10)より
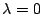 .
.
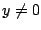 のとき,式(7.11)より
のとき,式(7.11)より
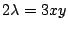 .式(7.10)に代入して,
.式(7.10)に代入して,
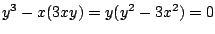 より
より
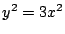 .式(7.9)に代入して
.式(7.9)に代入して
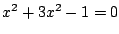 より
より
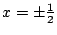 .よって,
.よって,
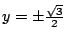 .したがって,式(7.9),(7.10),(7.11)の解は,
.したがって,式(7.9),(7.10),(7.11)の解は,
このとき,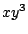 の値は,
の値は,
一方,
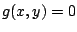 は有界閉集合で,この上で
は有界閉集合で,この上で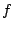 は連続だから最大値,最小値を持つ.以上より,最大値は
は連続だから最大値,最小値を持つ.以上より,最大値は
最小値は
(b)
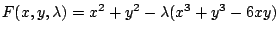 とおくと
とおくと
式(7.12),(7.13)より
よって,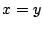 ,または,
,または,
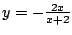 .
.
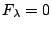 より
より
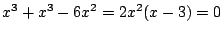 .したがって,
.したがって,
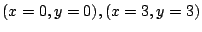 .
一方,
.
一方,
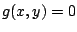 の第1象限の部分に原点をつけ加えたものは有界閉曲線で,
の第1象限の部分に原点をつけ加えたものは有界閉曲線で,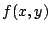 はその上で連続だから最大値,最小値を持つ.以上より,最大値は
はその上で連続だから最大値,最小値を持つ.以上より,最大値は
又,
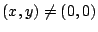 なら
なら
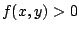 であるから,
であるから,
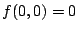 が極小値かつ最小値である.
が極小値かつ最小値である.
(c)
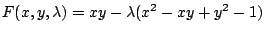 とおくと
とおくと
式(7.16),(7.17)より
よって,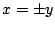 .
.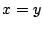 のとき
のとき
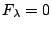 より
より
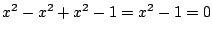 .したがって,
.したがって,
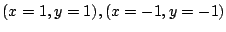 .
.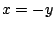 のとき
のとき
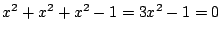 .したがって,
.したがって,
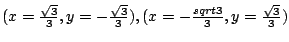 .
このとき,
.
このとき,
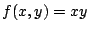 の値は,
の値は,
一方,
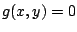 は有界閉集合で,この上で
は有界閉集合で,この上で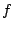 は連続だから最大値,最小値を持つ.以上より,最大値は
は連続だから最大値,最小値を持つ.以上より,最大値は
最小値は
3.
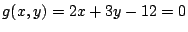 とおくと
とおくと
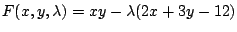 .
.
式(7.19),(7.20)より
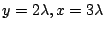 .これを式(7.18)に代入すると
.これを式(7.18)に代入すると
よって,
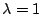 より
より
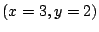 .一方,
.一方,
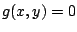 は有界閉集合で,この上で
は有界閉集合で,この上で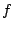 は連続だから最大値を持つ.以上より,最大値は
は連続だから最大値を持つ.以上より,最大値は
4.
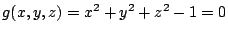 とおくと
とおくと
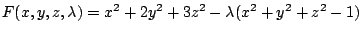 .
.
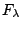 |
 |
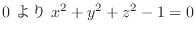 |
(7.21) |
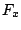 |
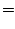 |
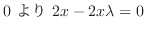 |
(7.22) |
 |
 |
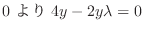 |
(7.23) |
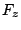 |
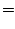 |
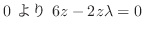 |
(7.24) |
式(7.22),(7.23),(7.24)より
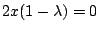 ,
,
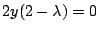 ,
,
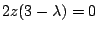 .ここで,
.ここで,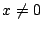 とすると,
とすると,
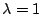 より
より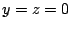 .これを式(7.21)に代入すると
.これを式(7.21)に代入すると
よって,
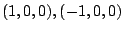 .
.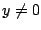 とすると,
とすると,
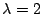 より
より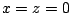 .これを式(7.21)に代入すると
.これを式(7.21)に代入すると
よって,
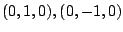 .
.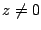 とすると,
とすると,
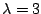 より
より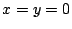 .これを式(7.21)に代入すると
.これを式(7.21)に代入すると
よって,
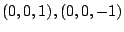 .これより式(7.21)の値を求めると
.これより式(7.21)の値を求めると
一方,
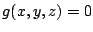 は有界閉集合で,この上で
は有界閉集合で,この上で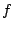 は連続だから最大値,最小値を持つ.以上より,最大値は
は連続だから最大値,最小値を持つ.以上より,最大値は
また,最小値は
![]() より定まる陰関数
より定まる陰関数![]() が
が![]() で極値
で極値
![]() をとるならば,
をとるならば,
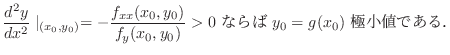
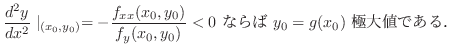
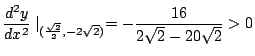
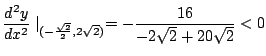
![]() のとき
のとき
![]() は極小値,
は極小値,
![]() のとき
のとき
![]() は極大値.
は極大値.
![]() を満たす
を満たす![]() を求める.
を求める.
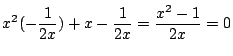
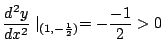
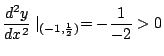
![]() のとき
のとき
![]() は極小値,
は極小値,![]() のとき
のとき
![]() も極小値.
も極小値.
![]() を満たす
を満たす![]() を求める.
を求める.
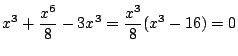
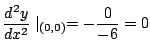
![$\displaystyle \frac{d^2 y}{dx^2}\mid_{(2\sqrt[3]{2}, 2\cdot2^{\frac{2}{3}})} = -\frac{6\cdot 2\sqrt[3]{2}}{-6} > 0$](img2370.gif)
![]() のとき
のとき
![]() は極小値.
は極小値.
![]() と
と
![]() の少なくとも一方は0でないとする.
条件
の少なくとも一方は0でないとする.
条件
![]() の元で,
の元で,![]() が
が
![]() で極値をとるための必要条件は
で極値をとるための必要条件は
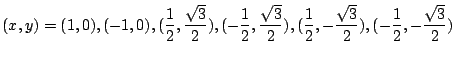
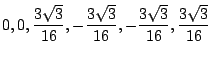
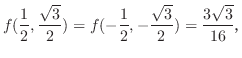
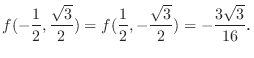
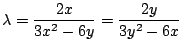
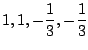
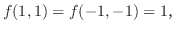
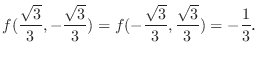
![]() とおくと
とおくと
![]() .
.