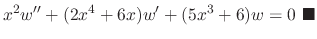Next: Exercise Up: Linear Differential Equations Previous: Exercise Contents Index
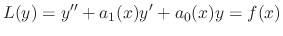
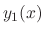 of
of 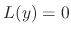 is known. Then substitute
is known. Then substitute
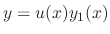 into
into
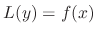 .
.
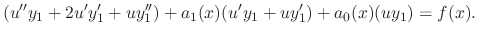
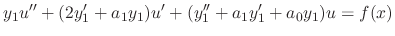
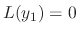 , we note that the coefficient of
, we note that the coefficient of 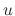 is 0. Now let
is 0. Now let
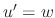 . Then we have a 1st order linear differential equation in
. Then we have a 1st order linear differential equation in 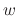 .
.
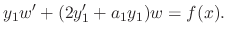
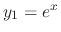 is a solution of
is a solution of
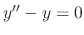 , find the general solution of
, find the general solution of
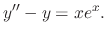
SOLUTION
Let
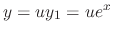 . Then
. Then
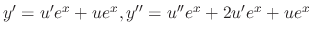 .
Substitute these into
.
Substitute these into
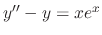 . Then
. Then
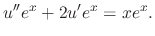
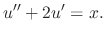
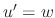 . Then we have the following linear differential equation in
. Then we have the following linear differential equation in 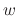 .
.
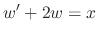
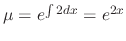 and
and
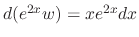 .
Integrate this with respect to
.
Integrate this with respect to 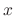 to get
to get
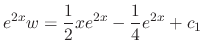
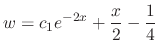
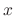
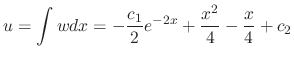
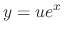 , the general solution is
, the general solution is
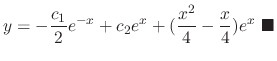
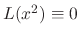 , Reduce the order of the following differential equation
, Reduce the order of the following differential equation
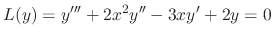
SOLUTION
Let
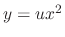 . Then
. Then
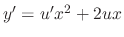 ,
,
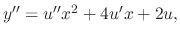
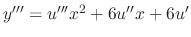 . Thus
. Thus
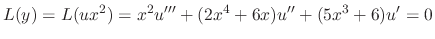
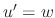 . Then
. Then