Next: Partial Differentiation of Composite Up: Total Differential and Tangent Previous: Total Differential and Tangent Contents Index
If
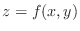 is totally differentiable at
is totally differentiable at 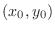 , then
, then
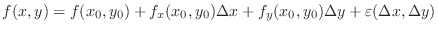
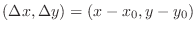 .
Note that
.
Note that
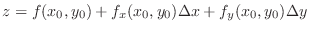
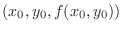 . Note also that these two equations behave almost the same when
. Note also that these two equations behave almost the same when 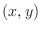 is close to
is close to 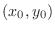 . Thus the equation above is called tangent plane of the function
. Thus the equation above is called tangent plane of the function
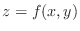 at
at
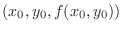 .
.
NOTE Given the point
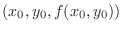 and take a point
and take a point 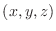 . Then we can form a vector
. Then we can form a vector
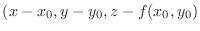 . Now
. Now
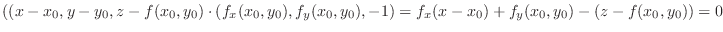 Thus
Thus
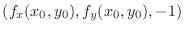 is orthogonal to the tangent plane.
is orthogonal to the tangent plane.
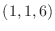 .
.
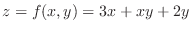
SOLUTION
Since
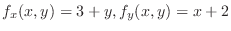 , the tangent plane of
, the tangent plane of 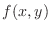 at
at 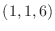 is given by the following.
is given by the following.
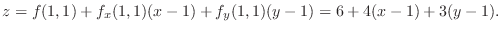
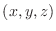 be an arbitray point on the normal line. Then the vector connecting
be an arbitray point on the normal line. Then the vector connecting 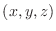 and
and 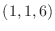 is given by
is given by
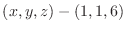 and this vector
and this vector
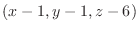 is on the normal line with the normal vector
is on the normal line with the normal vector 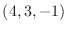 , Thus the normal line is
, Thus the normal line is
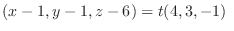 or
or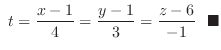
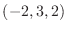 .
.
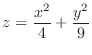
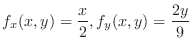 , the tangent plane of
, the tangent plane of 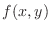 at
at 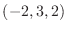 is given by
is given by
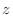 |
 |
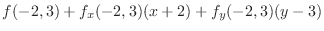 |
|
 |
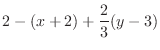 |
||
 |
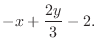 |
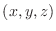 be an arbitray point on the normal line. Then the vector connecting
be an arbitray point on the normal line. Then the vector connecting 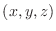 and
and 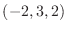 is given by
is given by
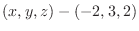 and this vector
and this vector
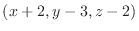 is on the normal line with the normal vector
is on the normal line with the normal vector
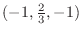 , Thus the normal line is
, Thus the normal line is
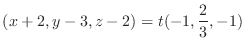
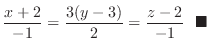
(a) Find the equation of the tangent plane to the surface whose normal vector is 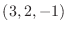 . Find the equation of the normal line through the point
. Find the equation of the normal line through the point 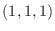 .
.
(b) Find the equation of the tangent plane to the surface 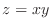 at the point
at the point 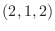 . Find the equation of the normal line through the point
. Find the equation of the normal line through the point 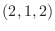 .
.
(c) Find the equation of the tangent plane to the surface
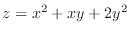 at the point
at the point 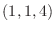 . Find the equation of the normal line through the point
. Find the equation of the normal line through the point 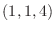 .
.
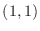 . Find the equation of the normal line at the point corresponds to
. Find the equation of the normal line at the point corresponds to 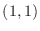 .
.