Next: Change of Variables Up: Multiple Integrals Previous: Double Integrals Contents Index
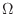 bounded by
bounded by
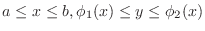 is called Vertically simple region,
The closed region
is called Vertically simple region,
The closed region 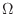 bounded by
bounded by
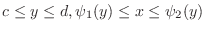 is called Horizontally simple region.
is called Horizontally simple region.
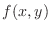 is continuous on the closed region
is continuous on the closed region
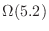 bounded by
bounded by
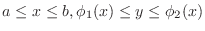 , then
, then
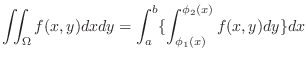
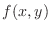 is continuous on the closed region
is continuous on the closed region
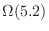 bounded by
bounded by
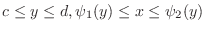 , then
, then
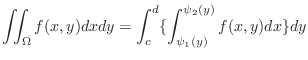
SOLUTION When a horizontal line is drawed to the region
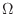 , it intersects the curve more than once. But when a vertical line is drawed to the region
, it intersects the curve more than once. But when a vertical line is drawed to the region 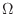 , it does not intersect more than once. Thus the region is vertically simple region.
Now fix
, it does not intersect more than once. Thus the region is vertically simple region.
Now fix 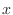 . Then the region is in between the curve
. Then the region is in between the curve 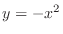 and the curve
and the curve 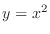 . Thus we have
. Thus we have
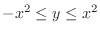 . Next free
. Next free 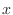 to get
to get
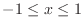 . Thus
. Thus 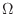 is expressed as follows.
is expressed as follows.
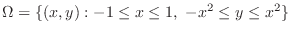
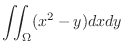 |
 |
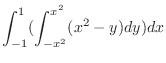 |
|
 |
![$\displaystyle \int_{-1}^{1}\left[(x^2 y - \frac{1}{2}y^2) \right ]_{-x^2}^{x^2} dx$](img1114.png) |
||
 |
![$\displaystyle \int_{-1}^{1}[(x^4 - \frac{1}{2}x^4) - (-x^4 - \frac{1}{2}x^4)]dx$](img1115.png) |
||
 |
![$\displaystyle \int_{-1}^{1}2x^4dx = \left[\frac{2}{5}x^5 \right ]_{-1}^{1} = \frac{4}{5}
\ensuremath{ \blacksquare}$](img1116.png) |
SOLUTION This region is both vertically simple region and horizontally simple region. We first evaluate the integral by using vertically simple region.
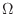 can be expressed by the following.
can be expressed by the following.
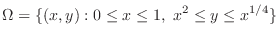
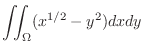 |
 |
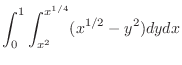 |
|
 |
![$\displaystyle \int_{0}^{1}\left[x^{1/2}y - \frac{1}{3}y^3\right ]_{x^2}^{x^{1/4}}dx$](img1124.png) |
||
 |
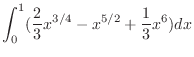 |
||
 |
![$\displaystyle \left[\frac{8}{21}x^{7/4} - \frac{2}{7}x^{7/2} + \frac{1}{21}x^7\right ]_{0}^{1}$](img1126.png) |
||
 |
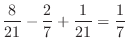 |
This time, we evaluate the integral by using horizontally simple region. 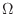 can be expressed by the following.
can be expressed by the following.
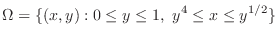
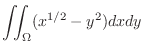 |
 |
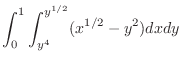 |
|
 |
![$\displaystyle \int_{0}^{1}\left[\frac{2}{3}x^{3/2} - y^2 x\right ]_{y^4}^{y^{1/2}}dy$](img1133.png) |
||
 |
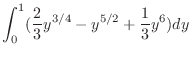 |
||
 |
![$\displaystyle \left[\frac{8}{21}y^{7/4} - \frac{2}{7}y^{7/2} + \frac{1}{21}y^7\right ]_{0}^{1}$](img1135.png) |
||
 |
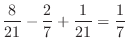 |

Interchage from vertically simple region to horizontally simple region or vice versa. Then corresponding integral change the order of integration.
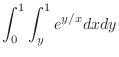
SOLUTION We can not evaluate the integral
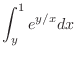 . Then by the change the order of integration, the region
. Then by the change the order of integration, the region  is given by
is given by
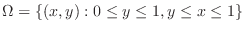
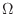 by the vertically simple region.
by the vertically simple region.
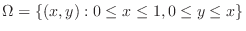
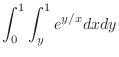 |
 |
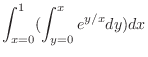 |
|
 |
![$\displaystyle \int_{0}^{1}[xe^{y/x}]_{0}^{x} dx$](img1144.png) |
||
 |
![$\displaystyle \int_{0}^{1}(xe - x)dx = \left[\frac{(e-1)x^2}{2}\right]_{0}^{1} = \frac{e-1}{2}\ensuremath{ \blacksquare}$](img1145.png) |
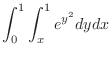
SOLUTION Note that
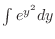 is known for non-integrable. Thus it is impossible to integrate
is known for non-integrable. Thus it is impossible to integrate
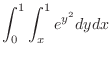 in this order. Thus, interchange the order of integration. Since
in this order. Thus, interchange the order of integration. Since
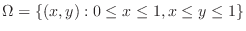
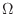 by the horizontally simple region.
by the horizontally simple region.
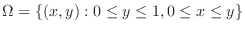
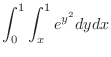 |
 |
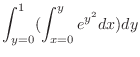 |
|
 |
![$\displaystyle \int_{0}^{1}[xe^{y^{2}}]_{0}^{y} dy$](img1157.png) |
||
 |
![$\displaystyle \int_{0}^{1}ye^{y^{2}} dy = \left[\frac{1}{2}e^{y^2}\right]_{0}^{1} = \frac{e-1}{2}\ensuremath{ \blacksquare}$](img1158.png) |
(a) Find the volume of solid bounded by the following surface under the surface 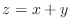 and above the triqngle
and above the triqngle
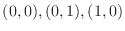
(b) Find the volume of solid bounded by the following surface under the surface 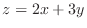 and qbove the square
and qbove the square
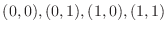 .
.
(c) Find the volume of the solid bounded above by the surface
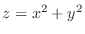 and below by the plane
and below by the plane
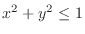
(d)
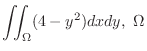 is bounded by
is bounded by 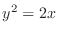 and
and
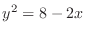 .
.