Next: Integration of Irrational Functions Up: Integration Previous: Integration of Rational Functions Contents Index
Integration of Trigonometric Functions[I]
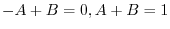
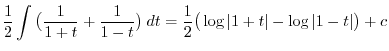 . Let
. Let
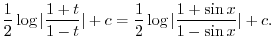 . Then
. Then
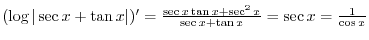 and
and
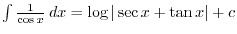
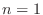 . Let
. Let
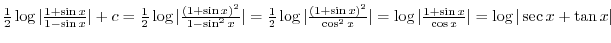 . Then
. Then
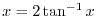 and
and
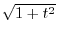
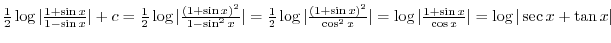 . Thne
. Thne
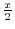 ,
,
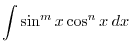
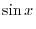
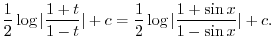 . Then
. Then
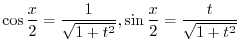 .
.
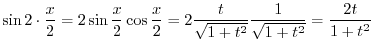
Integration of Trigonometric Functions[I]
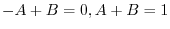
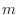 is odd, then
is odd, then 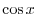 is even. Using
is even. Using
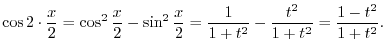 , express
, express
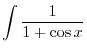 as in the form of
as in the form of  . Thus,
. Thus,
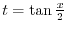
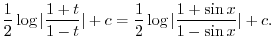 . Then
. Then
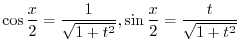 and
and
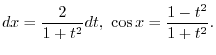

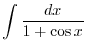
Similarly for 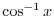 odd.
odd.
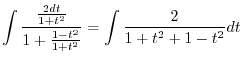
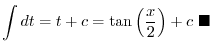 is odd power of
is odd power of 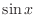 ,
,
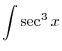
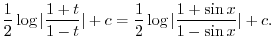 . Then
. Then
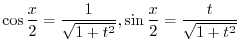 and
and
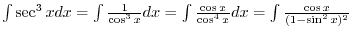 |
 |
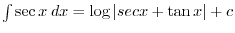 |
|
 |
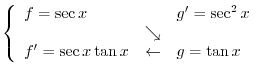 |
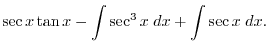 .
.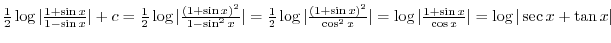 . Then
. Then
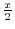 and
and
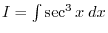 |
 |
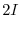 |
|
 |
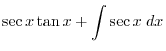 |
||
 |
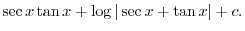 |
||
 |
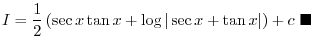 |
Integration of Trigonometric Function[I]
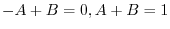
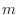 and
and  are both even. Now let
are both even. Now let
 . Then we can express
. Then we can express
 by using
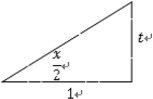
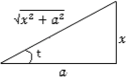
by using  . Consider the right triangle with the adjacent of the angle
. Consider the right triangle with the adjacent of the angle 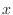 is 1 and the opposite is
is 1 and the opposite is 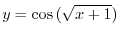 . Then
. Then
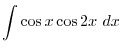 and
and
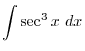
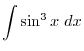
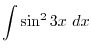
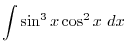
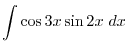 2.
2.
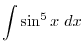
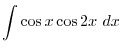 , it is easier to use double angle formula.
, it is easier to use double angle formula.
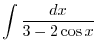
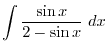



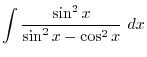

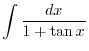
2. Let
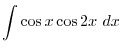 . Then
. Then
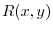 ,
,
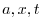 ,
,
 . Thus
. Thus


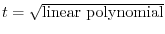

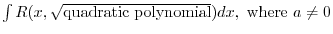
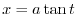 2.
2.
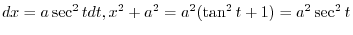
1. Let
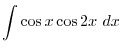 and express
and express
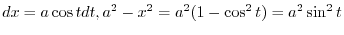 . Then
. Then
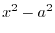
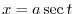 |
 |
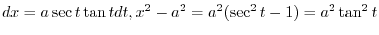 |
|
 |
![$\displaystyle \int \frac{1 + t^{2} - 1}{1+ t^{2}} dt = \int [1 - \frac{1}{1+ t^2}] dt$](img2761.png) |
||
 |
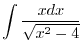 |
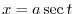 |
 |
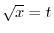 |
|
 |
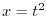 |
2.
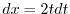 . Then it is in the form of [1]-2.
. Then it is in the form of [1]-2.
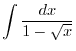 |
 |
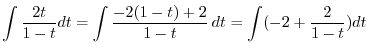 |
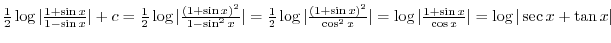 and
and
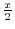
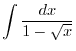 |
 |
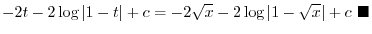 |
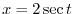
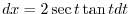
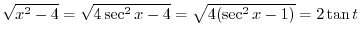 . Then
. Then
 .
Thus,
.
Thus,
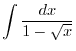 |
 |
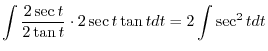 |
|
 |
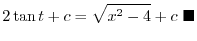 |
| Integration of Trigonometric Functions[II] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
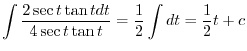
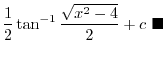 . Then . Then
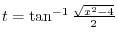 ,the adjacent to the angle 1, and opposite to the angle ,the adjacent to the angle 1, and opposite to the angle 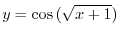 . .
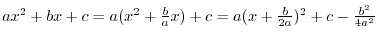
|
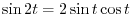 .
. 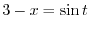 ,
,
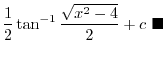 .
.
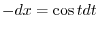
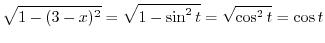 |
 |
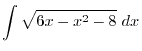 |
|
 |
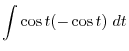 |
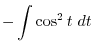 .
.
SOLUTION
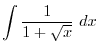
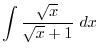 |
 |
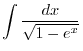 |
|
 |
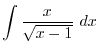 |
||
 |
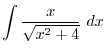 |
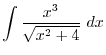 . Then
. Then
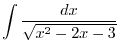 |
 |
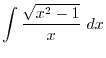 |
|
 |
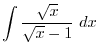 |
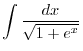
|
Exercise A
|
|
Exercise B
|