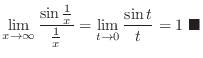Next: One sided limit Up: Functions Previous: Limit of Sequence Contents Index
NOTE Intuitive approach to limit
As 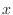 approaches
approaches 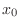 ,
, 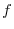 approaches
approaches 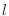 , Then we say
, Then we say 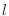 is the limit of
is the limit of 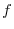 as
as 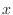 approaches
approaches 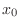 and denote
and denote
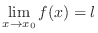
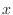 approaches
approaches 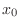 is the same as
is the same as
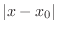 approaches 0. Similarly,
approaches 0. Similarly, 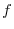 approaches
approaches 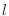 is the same as
is the same as
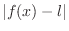 approaches 0.
approaches 0.
Limit properties
NOTE Limit of functions obey the four rules of arithmetic provided the denominator is not 0.
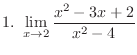
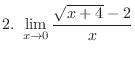
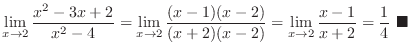 |
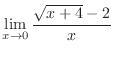 |
 |
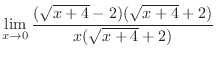 |
|
 |
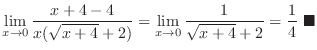 |
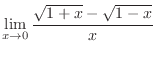
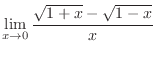 |
|||
 |
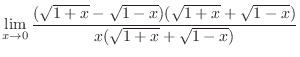 |
||
 |
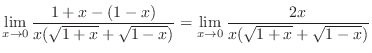 |
||
 |
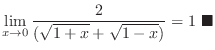 |
Diverges to infinity
We write
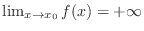 when
when 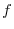 gets larger without bound as
gets larger without bound as 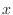 approaches
approaches 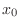 .
We write
.
We write
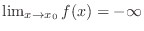 when the value of
when the value of 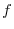 is negative and the absolute value gets larger without bound as
is negative and the absolute value gets larger without bound as 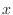 approaches
approaches 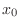 .
.
NOTE 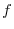 gets larger without bound means that given any large number
gets larger without bound means that given any large number 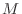 , there exists number
, there exists number 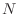 such that
such that 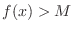 as
as 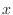 gets larger than
gets larger than 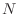 .
We write
.
We write
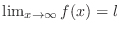 when
when 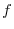 approaches
approaches 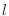 as
as 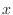 gets larger without bound.
gets larger without bound.
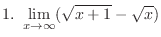
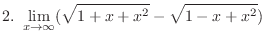
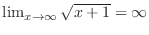 ,
,
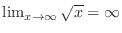 . Thus it is indeterminate form of
. Thus it is indeterminate form of
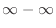 .
.
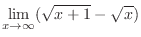 |
 |
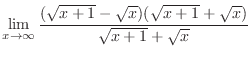 |
|
 |
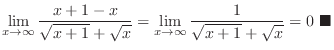 |
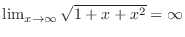 ,
,
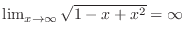 . Thus it is indeterminate form of
. Thus it is indeterminate form of
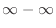 . Now rationalize the fraction
. Now rationalize the fraction
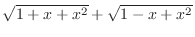 .
.
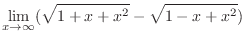 |
|||
 |
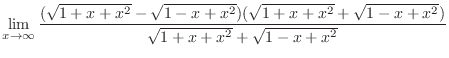 |
||
 |
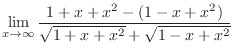 |
||
 |
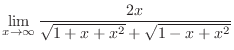 |
||
 |
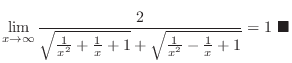 |
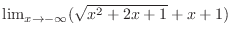
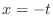 . Then
. Then
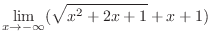 |
 |
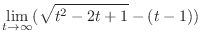 |
|
 |
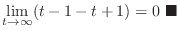 |
To find the limit of function, the above theorem is not enogh. For example
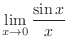 can not be found..
can not be found..
NOTE
Since
Squeezing theorem
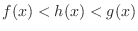 is satisfied for the
is satisfied for the 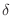 neighborhood
neighborhood
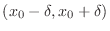 of
of 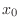 and
and
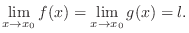
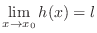 .
. 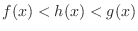 ,
,
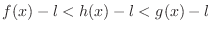 . Note that
. Note that
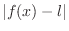 and
and
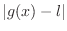 can be made as small as possible. Thus we can make
can be made as small as possible. Thus we can make
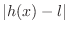 as small as possible .
as small as possible .
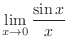 .
. 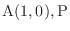 on the unit circle. Now find the intersection of the extended line OP and the line perpendicular to the line OA. We name the intersection B. Also, start from P, find the intersection of the line perpendicular to OA, we name this C. Now we compare the size of the triangles. Then
on the unit circle. Now find the intersection of the extended line OP and the line perpendicular to the line OA. We name the intersection B. Also, start from P, find the intersection of the line perpendicular to OA, we name this C. Now we compare the size of the triangles. Then
 .
Now for
.
Now for
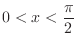 , we have
, we have
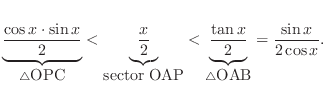
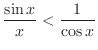 , and the second inequality
, and the second inequality
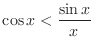 .
Thus
.
Thus
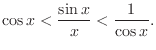
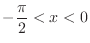 .
Now we have
.
Now we have
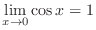 and
and
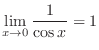 . Therefore,
. Therefore,
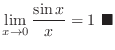
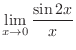 .
. 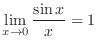 imples that for
imples that for 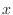 small,
small, 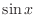 and
and 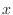 is about the same.
is about the same.
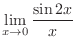 |
 |
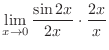 |
|
 |
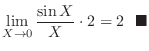 |
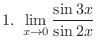
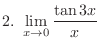
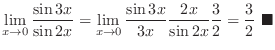
2.
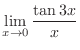 |
 |
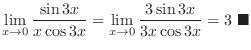 |
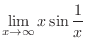 .
. 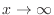 ,
,
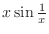 has the indeterminate form
has the indeterminate form
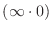 . Then we make this into the indeterminate form of
. Then we make this into the indeterminate form of
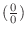 .
.
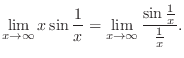
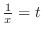 . Then as
. Then as
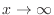 , we have
, we have 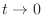 . Thus,
. Thus,