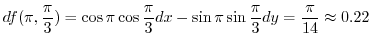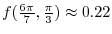Next: Gradient and directional derivatives Up: PARTIAL DIFFERENTIATION Previous: Total differential 索引
6.4
1.
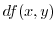 |
 |
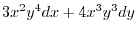 |
|
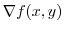 |
 |
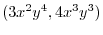 |
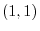 is
is
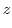 |
 |
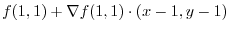 |
|
 |
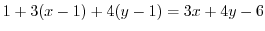 |
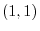 is
is
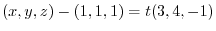
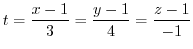
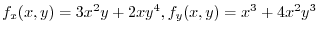 implies
implies
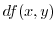 |
 |
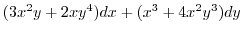 |
|
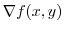 |
 |
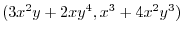 |
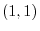 is
is
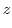 |
 |
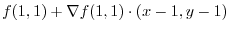 |
|
 |
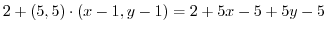 |
||
 |
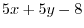 |
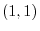 is
is
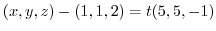
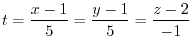
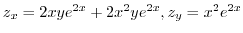 より
より
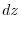 |
 |
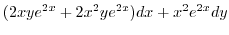 |
|
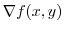 |
 |
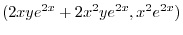 |
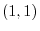 is
is
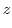 |
 |
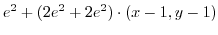 |
|
 |
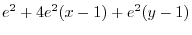 |
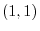 is
is
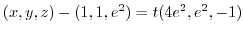
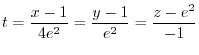
2.
(a)
Consider
![$f(x,y) = \sqrt{x}\sqrt[4]{y}$](img166.png) . Then
. Then
![$f(121,16) = \sqrt{121}\sqrt[4]{16} = 22$](img167.png) .Then the seeking vlaue is
.Then the seeking vlaue is
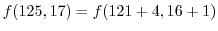 .Now let
.Now let
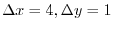 . Then
. Then
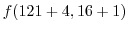 |
 |
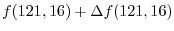 |
|
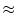 |
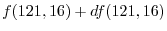 |
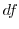 |
 |
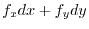 |
|
 |
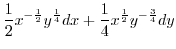 |
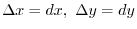 Then
Then
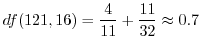
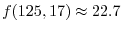
(b)
Consider
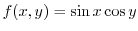 . Then
. Then
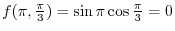 .The seeking value is
.The seeking value is
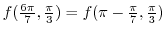 .Now let
.Now let
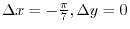 . Then
. Then
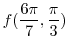 |
 |
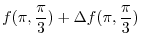 |
|
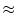 |
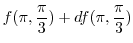 |
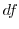 |
 |
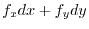 |
|
 |
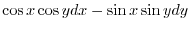 |
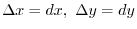 Thus,
Thus,