Next: Nonhomogeneous Differential Equations Up: System of Linear Differentia Previous: System of Homogeneous Linear 目次 索引
Answer
1.
(a)
 .
Then the eigenvalues are
.
Then the eigenvalues are
 . Now we find the eigenvector
. Now we find the eigenvector  corresponds to
corresponds to
 .
.

 is row reduced echelon form and no leading one in the 2nd row. So, we let
is row reduced echelon form and no leading one in the 2nd row. So, we let
 . Then
. Then
 . Thus the eigenvector is
. Thus the eigenvector is
 . Now we find the real part and the imaginary part of
. Now we find the real part and the imaginary part of
 .
.
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
||
 |
 |

(b)
 Then the eigenvalues are
Then the eigenvalues are
 . Now we find the eigenvector
. Now we find the eigenvector  corrsponds to
corrsponds to
 .
.


 とおくと,
とおくと,
 . Thus the eigenvector is
. Thus the eigenvector is
 . We next find the eigenvector corresponds to
. We next find the eigenvector corresponds to
 and linearly independent from
and linearly independent from  . Note that if we can find
. Note that if we can find  which satisfies
which satisfies


 . Then this matrix satifies
. Then this matrix satifies
 . Furthermore, we choose
. Furthermore, we choose
 so that
so that
 . Then
. Then
 . and the 2nd solution is
. and the 2nd solution is
 |
 |
![$\displaystyle e^{4t}e^{(A-4I)t}{\bf C} = e^{4t}[{\bf C} + t(A - 4I){\bf C} + \frac{t^2}{2!}(A - 4I)^2 {\bf C}]$](img1265.png) |
|
 |
 |
 are linearly independent. The general solution can be expressed as follows:
are linearly independent. The general solution can be expressed as follows:
![$\displaystyle {\bf X} =e^{4t}[c_{1}\left(\begin{array}{c}
1\\
-2
\end{array}\right) + c_{2}\left(\begin{array}{c}
1-3t\\
1+6t
\end{array}\right)] \ $](img1268.png)
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 .
.
 corresponds to
corresponds to
 is nonzero solution of the equation
is nonzero solution of the equation
 . Using Gaussian elimination,
. Using Gaussian elimination,
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 .
.

 .
.
Next we find the eigenvector corresponds to
 .
.

 .
.


 are linearly independent. Thus , the general solution is given by
are linearly independent. Thus , the general solution is given by

 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 .
.
Now we find the eigenvector  corresponds to
corresponds to
 using Guassian elimination.
using Guassian elimination.
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 . Then
. Then

 .
.
We next find the eigenvector  corresponds to
corresponds to
 .
.
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 .,
.,

 . Thus, we need to find the real part and the imaginary part of
. Thus, we need to find the real part and the imaginary part of
 .
.
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |


 . Then
. Then
 and
and
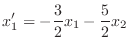 |
(3.1) |
 . Then
. Then
 and
and
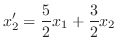 |
(3.2) |

 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 .
.
We find the eigenvector corresponds to
 using Gaussian elimination.
using Gaussian elimination.
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 .
.

 .
.
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |


 . Thus,
. Thus,

 . Now we find the eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
. Now we find the eigenvalues and eigenvectors.

 .
.
We find the eigenvector  corresponds to
corresponds to
 using Gaussian elimination.
using Gaussian elimination.

 .
.

 .
.
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
![$\displaystyle {\bf X} = e^{-t}[c_{1}\left(\begin{array}{c}
-2\cos{t}-\sin{t}\\ ...
...+ c_{2} \left(\begin{array}{c}
\cos{t}-2\sin{t}\\
\sin{t}
\end{array}\right)] $](img1351.png)