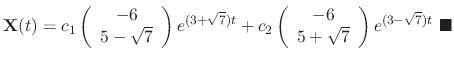Next: Exercise Up: Systems of differential equations Previous: Systems of differential equations Contents Index
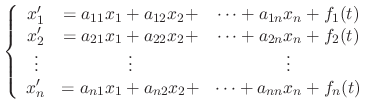
 and the column vector
and the column vector 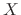 anf
anf 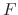 , we can express
, we can express
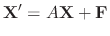
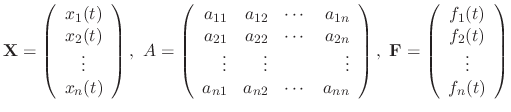
The differentiable functions
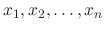 satisfying the above equation is called the solution. When
satisfying the above equation is called the solution. When
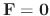 , we say that the differential equation is homogeneous equation.
, we say that the differential equation is homogeneous equation.
We will explain how to solve
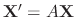 .
Let
.
Let
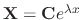 . Then
. Then
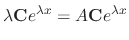
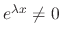 , we have
, we have
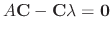
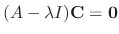
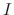 denotes the unit matrix of the degree
denotes the unit matrix of the degree 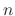 .
Now if
.
Now if
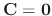 , then the equation is obviously satisfied. So, we need to find the
, then the equation is obviously satisfied. So, we need to find the
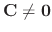 satisfying the above equation.
Note that if
satisfying the above equation.
Note that if
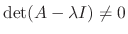 , then
, then
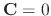 . Thus to find the
. Thus to find the
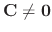 , we have to solve
, we have to solve
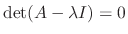 .
The
.
The 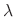 is called the eigenvalue of the matrix
is called the eigenvalue of the matrix 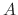 and the nonzero C satisfying
and the nonzero C satisfying
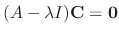 is called the eigenvector for
is called the eigenvector for 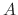 .
.
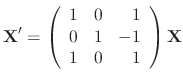
SOLUTION
Let
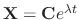 . Then we have
. Then we have
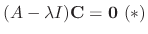
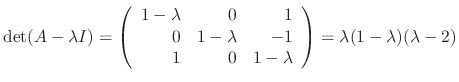
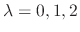 .
Now we find the eigenvector for
.
Now we find the eigenvector for
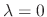 . Substitute
. Substitute
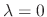 into the equation (*). Then
into the equation (*). Then
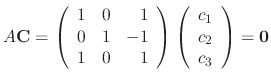
 |
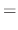 |
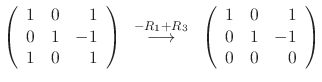 |
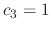 . Then
. Then
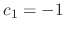 ,
, 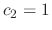 Thus, the eigenvector C is
Thus, the eigenvector C is
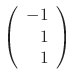 and
and
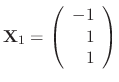 is a solution.
is a solution.
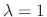 .
.
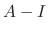 |
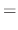 |
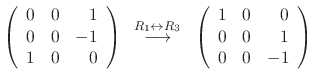 |
|
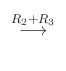 |
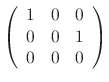 |
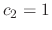 . Then
. Then 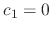 ,
, 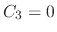 and the eigenvector is
and the eigenvector is
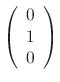 .
.
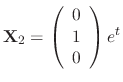 is a solution. Similarly, we find the eigenvector corresponds to
is a solution. Similarly, we find the eigenvector corresponds to
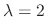
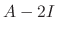 |
 |
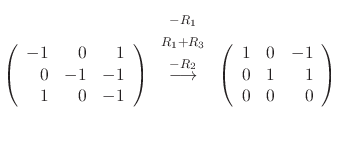 |
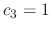 and
and
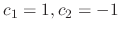 . Thus the eigenvector is
. Thus the eigenvector is
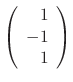 .
.
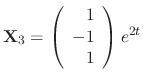 is a solution. Since
is a solution. Since
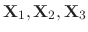 are linearly independent, we have
are linearly independent, we have
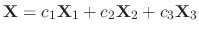 and the general solution is
and the general solution is
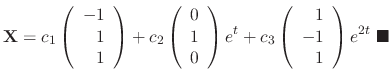
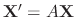 has the
has the 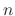 different eigenvalues
different eigenvalues
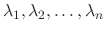 and corresponding eigenvectors
and corresponding eigenvectors
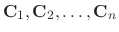 . Then the general solution is given by
. Then the general solution is given by
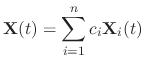
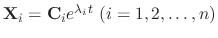 are the solutions of
are the solutions of
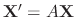 and linearly independent.
and linearly independent.
Proof
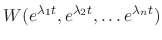 |
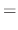 |
 |
|
 |
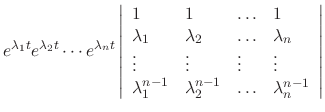 |
||
 |
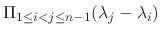 |
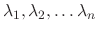 are different,
are different,
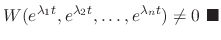
The 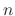 linearly independent solutions of
linearly independent solutions of
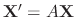 is called the fundamental solution.
is called the fundamental solution.
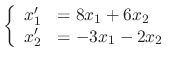 .
.
SOLUTION
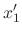 |
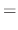 |
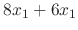 |
|
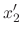 |
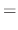 |
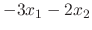 |
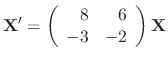
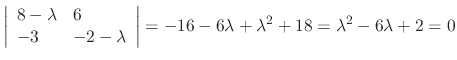
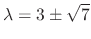 .
For
.
For
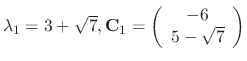 .
For
.
For
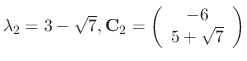 . Thus the general solution is
. Thus the general solution is