Next: Exercise Up: Linear Differential Equations Previous: Exercise Contents Index

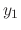 and
and 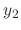 be the fundamental solution of
be the fundamental solution of 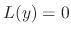 .
Let the particular solution be as follows
.
Let the particular solution be as follows

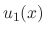 and
and 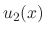 are undeterminded functions. To find
are undeterminded functions. To find 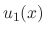 and
and 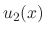 , we need two conditions.
The first condition is that
, we need two conditions.
The first condition is that
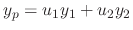 is a solution of
is a solution of
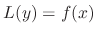 . The second condition is to make the calculation simple, that is,
. The second condition is to make the calculation simple, that is,
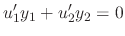
 and substitute into
and substitute into
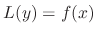 . Then
. Then
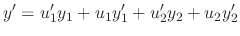
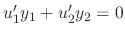 ,
,

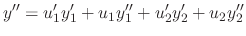
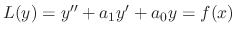 . Then
. Then

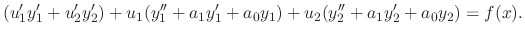
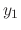 and
and 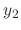 are solutons of
are solutons of 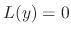 . Thus the coefficients of
. Thus the coefficients of  and
and 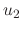 are 0. Therefore,
are 0. Therefore,
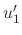 and
and
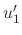 are solutions of the following system of equation.
are solutions of the following system of equation.
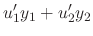 |
 |
0 | |
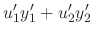 |
 |
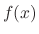 |
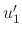 and
and  and then find
and then find 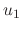 and
and  .
.
To solve the above system, we use the Cramer's rule. Then
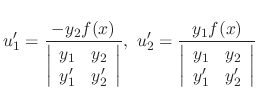
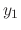 and
and 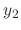 . Since
. Since 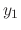 and
and 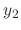 are linearly independent. Thus by the theorem 2.5, the Wronskian is never 0. Thus we can find
are linearly independent. Thus by the theorem 2.5, the Wronskian is never 0. Thus we can find
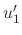 and
and
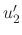 . By integrating with respect to
. By integrating with respect to 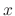 , we can find
, we can find  and
and 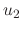 . Thus we can find
. Thus we can find
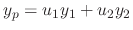 .
.
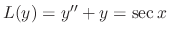 .
.
SOLUTION
The characteristic equation of 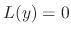 is
is
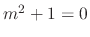 and thus the roots are
and thus the roots are  . Then the complementary solution is
. Then the complementary solution is
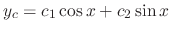
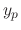 . Since
. Since
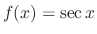 is not a solution of a homogeneous linear differential equation, we can not use the method of undetermined coefficients. So, we let
is not a solution of a homogeneous linear differential equation, we can not use the method of undetermined coefficients. So, we let
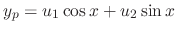
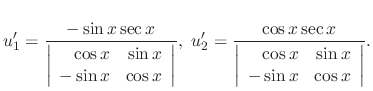
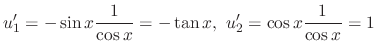
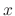 , we have
, we have


Suppose that
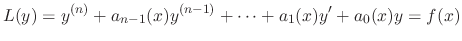
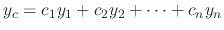 be the solution of
be the solution of
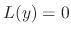 .
Now replace the constants
.
Now replace the constants
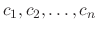 by the variables
by the variables
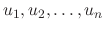 . Then
. Then
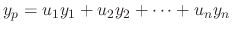
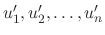 satisfy the following system.
satisfy the following system.
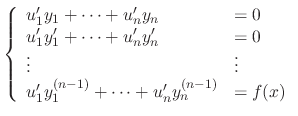
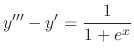
SOLUTION
The characteristic equation of
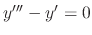 is
is
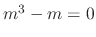 . Then roots are
. Then roots are
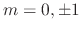 . Thus the complementary solution is
. Thus the complementary solution is
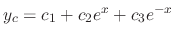
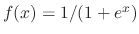 , we use the variation of parameter to find the particular solution. Let
, we use the variation of parameter to find the particular solution. Let
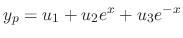
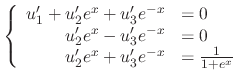
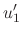 |
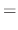 |
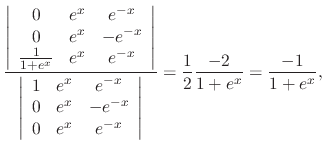 |
|
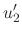 |
 |
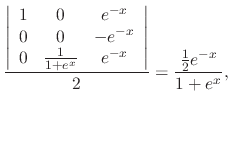 |
|
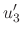 |
 |
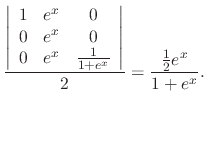 |
 |
 |
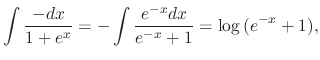 |
|
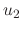 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
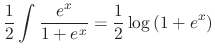 |
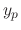 and we have the general solution
and we have the general solution
