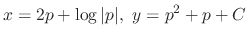Next: Exercise Up: 1st Order Differential Equation Previous: Exercise Contents Index
In mathematics, a differential equation of the form
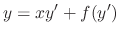
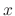 , yielding
, yielding
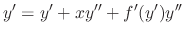
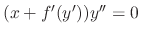 . Thus, either
. Thus, either 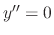 or
or
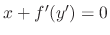 .
In the former case,
.
In the former case, 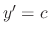 for some constant. Substituting this into the Clairaut's equation, we have the family of straight line functions given by
for some constant. Substituting this into the Clairaut's equation, we have the family of straight line functions given by
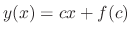 . The latter case
. The latter case
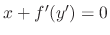 . We let
. We let
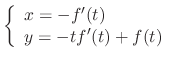 , where
, where 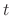 is a parameter. Then
is a parameter. Then
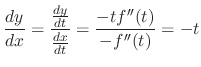
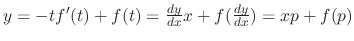 . Then this is a solution to the Clairaut's equation. If
. Then this is a solution to the Clairaut's equation. If
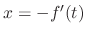 has a solution
has a solution 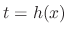 , then
, then
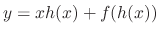 and a singular solution to
and a singular solution to
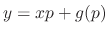 .
.
A differntial equation of the form
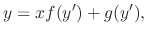
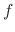 and
and 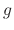 are function of
are function of 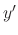 ,
is called D'Alembert equation.
To solve the D'Alembert's equation, we differentiate with respect to
,
is called D'Alembert equation.
To solve the D'Alembert's equation, we differentiate with respect to 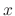 .
.
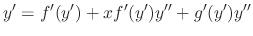
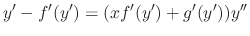
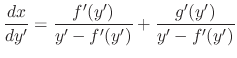
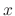 and independent variable in
and independent variable in 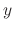 .
.
We use the following symbol for simplicity.
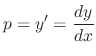
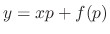
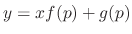
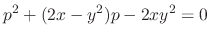
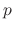 . By factorization, we obtain
. By factorization, we obtain
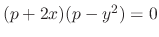 . This equation is satisfied by either
. This equation is satisfied by either
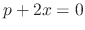 or
or
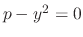 . Note that the general solution of
. Note that the general solution of 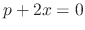 is
is
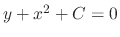 . Also,
. Also,
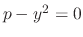 is separable differential equation. Thus we obtaine the general solution
is separable differential equation. Thus we obtaine the general solution
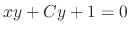 . Form this the general solution is
. Form this the general solution is
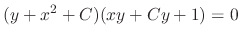
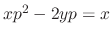 .
.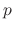 . Then by the quadratic formula, we have
. Then by the quadratic formula, we have
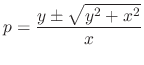
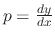 , this is homogeneous. Let
, this is homogeneous. Let 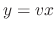 . Then
. Then
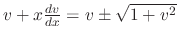 . Thus
. Thus
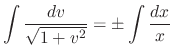
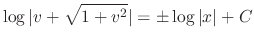
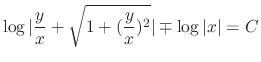
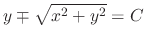
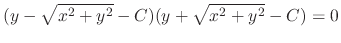
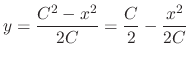
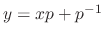 , where
, where 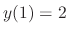
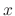 .
.
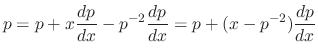
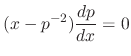
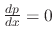 or
or
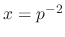 .
For the first case, we have
.
For the first case, we have 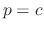 a some constant. Thus
a some constant. Thus
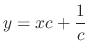
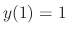 , we have
, we have
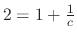 . Thus
. Thus
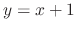
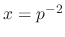 into the original equation. Then
into the original equation. Then
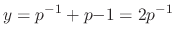
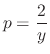
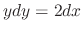
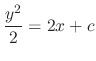
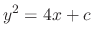
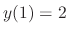 , we have
, we have 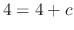 . Therefore, the singular solution is
. Therefore, the singular solution is
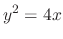
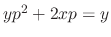 .
.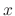 . Then
. Then
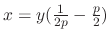 . Now differentiate with respect to
. Now differentiate with respect to 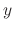 , Then
, Then
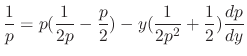
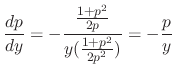
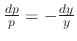 . Then
. Then
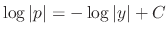 ,
, 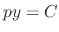 . From this, we have
. From this, we have
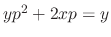 . Delete
. Delete 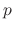 and we have the general solution
and we have the general solution
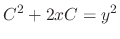
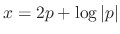 .
.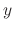 .
.
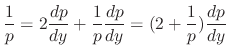
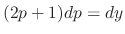
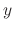
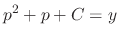
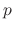 as a parameter,
as a parameter,